Seborrheic Dermatitis vs Dandruff vs Eczema vs Psoriasis: What’s the Difference?
When your skin feels itchy, flaky, or irritated, it’s easy to assume it’s just dandruff or dry skin. However, several skin conditions share similar symptoms—especially seborrheic dermatitis, dandruff, eczema, and psoriasis. Understanding the difference between them is key to finding the right treatment and keeping your skin healthy and comfortable.
In this blog, we’ll help you spot the differences, explore how they’re related, and clear up common confusion between these conditions.
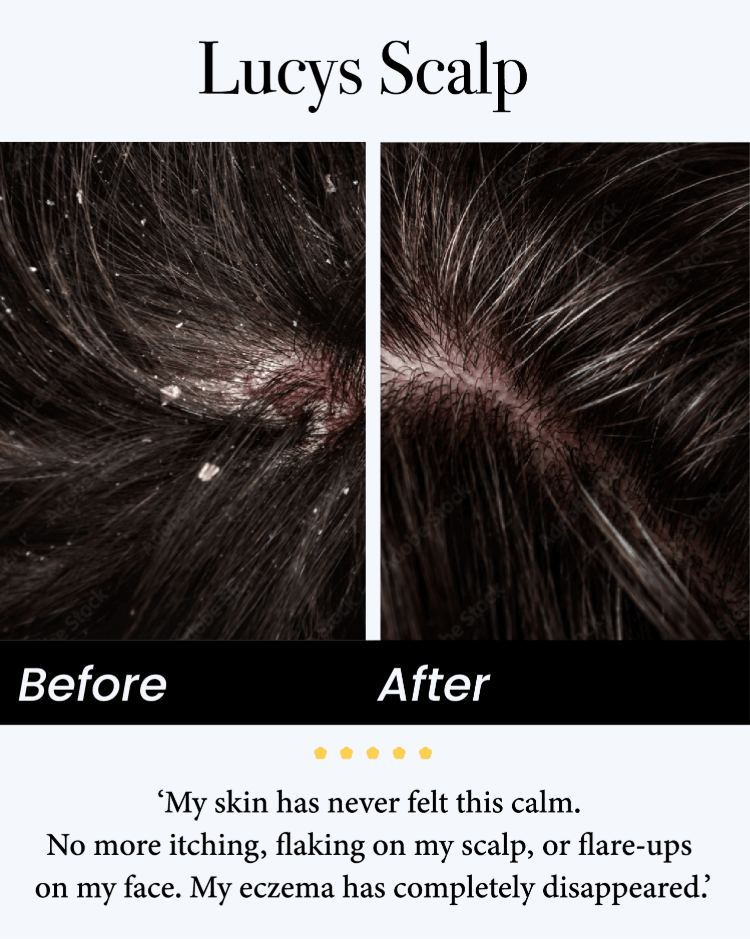
Seborrheic dermatitis is a chronic inflammatory skin condition that affects areas rich in oil glands—like the scalp, face, ears, and chest. It often appears as red, greasy, and flaky patches that may itch or feel irritated.
It’s caused by a combination of factors such as excess oil production, yeast (Malassezia) overgrowth, genetics, and environmental triggers like stress or weather changes.
Common Signs:
- Yellowish or white flakes
- Red, inflamed patches (especially around the nose, eyebrows, or scalp)
- Itchiness or irritation in oily areas
Dandruff is often considered a milder form of seborrheic dermatitis that affects only the scalp. It leads to visible flakes without significant redness or inflammation.
Common Signs:
- White or grey dry flakes on the scalp
- Mild itching
- Flakes that worsen in cold, dry weather
Key Difference: Dandruff typically stays confined to the scalp, while seborrheic dermatitis can affect multiple parts of the body and tends to cause more redness and irritation.
Eczema, or atopic dermatitis, is a chronic allergic or immune-related skin condition that causes dryness, inflammation, and intense itching. Unlike seborrheic dermatitis, it’s not triggered by oil or yeast but rather by a weakened skin barrier and immune response.
Common Signs:
- Dry, rough, or cracked skin
- Severe itching (often worse at night)
- Rashes that can appear anywhere, especially behind knees, on elbows, and hands
Key Difference: Eczema is usually drier and itchier, with little to no oiliness. Seborrheic dermatitis tends to appear greasy and affects oil-rich areas.
Psoriasis is an autoimmune condition where the skin cells multiply too quickly, creating thick, scaly patches. It can appear similar to seborrheic dermatitis but is generally thicker, drier, and has more defined edges.
Common Signs:
- Thick, silvery-white scales
- Well-defined red plaques
- Commonly affects the scalp, elbows, knees, and lower back
Key Difference: Psoriasis scales are thicker and more persistent than seborrheic dermatitis flakes, and it often extends beyond the hairline.
While seborrheic dermatitis and rosacea can appear similar—especially on the face—they are distinct conditions that sometimes overlap.
- Seborrheic dermatitis involves flaking, redness, and oiliness, particularly around the nose, eyebrows, and scalp.
- Rosacea causes persistent redness, visible blood vessels, and sometimes acne-like bumps, usually on the central face.
However, some people experience both at the same time, as both involve skin inflammation and sensitivity. In these cases, treating one condition often helps improve the other.
Seborrheic dermatitis and eczema share many overlapping symptoms—itching, redness, and flaking—which is why they’re often mistaken for one another.
The main distinctions are:
- Skin texture: Seborrheic dermatitis is greasy and flaky, while eczema is dry, rough, and cracked.
- Common areas: Seborrheic dermatitis appears on the scalp, eyebrows, sides of the nose, and ears. Eczema is more common on the folds of the arms, behind the knees, and on the hands.
- Triggers: Seborrheic dermatitis is triggered by yeast, excess oil, and weather, whereas eczema is linked to allergies, irritants, and immune triggers.
- Age group: Seborrheic dermatitis can occur in both adults and infants, while eczema often starts in childhood.
In short, seborrheic dermatitis thrives in oily areas, while eczema is linked to dryness and a weakened skin barrier.
Although seborrheic dermatitis, dandruff, eczema, and psoriasis may look alike, their causes, triggers, and treatments differ. Getting a proper diagnosis from a dermatologist is the best way to manage your symptoms effectively.
With the right skincare routine—focused on barrier repair, gentle cleansing, and anti-inflammatory ingredients—you can soothe irritation, reduce flaking, and maintain balanced, healthy skin.