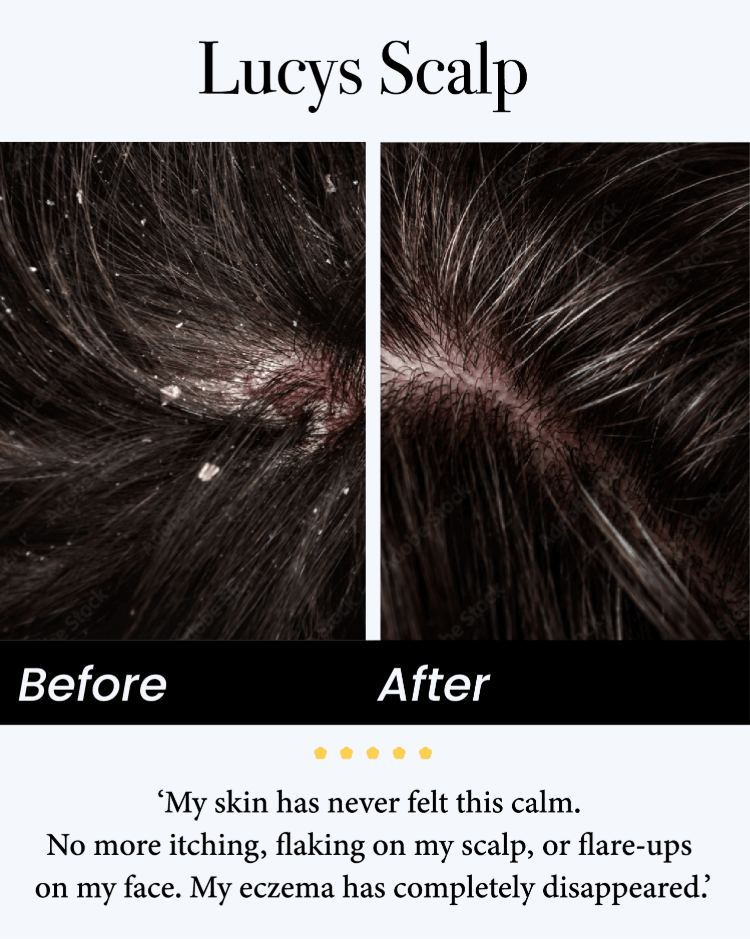
Eczema in Adults: Why It Can Appear Later in Life
Eczema, medically known as atopic dermatitis, is often associated with childhood. Most people think of it as a condition that starts early in life and sometimes fades as we grow older. However, a surprising number of adults experience eczema for the first time in their 30s, 40s, or even later. Understanding why eczema can appear later in life is essential for proper management and treatment.
What is Adult-Onset Eczema?
Adult-onset eczema refers to the occurrence of eczema symptoms for the first time in adulthood. While childhood eczema is typically linked to a family history of allergies, adult-onset eczema can appear even in people who never experienced skin problems as kids.
Symptoms may include:
-Red, inflamed skin
-Itching that can worsen at night
-Dry, scaly patches
-Thickened skin in chronic cases
-Possible oozing or crusting in flare-ups
Unlike childhood eczema, adult-onset eczema can sometimes appear in unusual areas, such as the hands, feet, eyelids, or the folds of the elbows and knees.
Why Eczema Can Appear Later in Life
-
Changes in the Immune System
As we age, our immune system evolves. Adult-onset eczema may be triggered by immune dysregulation, causing the skin to overreact to minor irritants or allergens. This is similar to how allergies can appear later in life. -
Environmental Triggers
Adults are exposed to different environments than children. Workplace irritants, chemicals, detergents, or even new skincare products can disrupt the skin barrier and trigger eczema. Stress, pollution, and seasonal changes also play a role. -
Hormonal Changes
Hormones can influence the immune response and skin health. Some adults develop eczema during periods of hormonal fluctuation, such as pregnancy, menopause, or thyroid disorders. -
Skin Barrier Dysfunction
Eczema is closely linked to a weakened skin barrier, which allows moisture to escape and irritants to penetrate. In adults, this barrier can be compromised by aging skin, frequent washing, harsh soaps, or certain medications. -
Underlying Health Conditions
Sometimes adult-onset eczema is associated with other conditions, such as asthma, allergic rhinitis, autoimmune disorders, or metabolic changes. Identifying underlying factors can help in effective treatment.
Differences Between Childhood and Adult Eczema
-Location: Children often have eczema on the face, scalp, and outer limbs. Adults may develop it on hands, eyelids, neck, and the torso.
-Severity: Adult eczema can sometimes be more persistent and resistant to standard treatments.
-Triggers: Adults are more affected by environmental factors, stress, and occupational exposures.
Managing Adult-Onset Eczema
Although adult eczema can be challenging, there are effective strategies for management:
-
Moisturise Regularly – Using fragrance-free, thick creams helps repair the skin barrier.
-
Identify Triggers – Keep a diary of flare-ups to spot irritants, allergens, or stress-related triggers.
-
Topical Treatments – Corticosteroids or calcineurin inhibitors may reduce inflammation.
-
Lifestyle Adjustments – Stress management, gentle skincare routines, and avoiding harsh detergents are crucial.
-
Medical Consultation – Severe or persistent cases may require phototherapy or systemic medications.
When to See a Dermatologist
If you notice persistent itching, red patches, or oozing lesions, it’s important to consult a dermatologist. Adult-onset eczema can sometimes mimic other conditions like psoriasis, fungal infections, or allergic contact dermatitis, making professional diagnosis essential.
Bottom Line
Eczema in adults may appear unexpectedly, even in people with no childhood history. Factors like immune changes, environmental exposures, hormonal shifts, and skin barrier issues all play a role. While adult-onset eczema can be frustrating, early diagnosis and proper management can significantly improve quality of life. Understanding triggers, maintaining healthy skin, and seeking professional guidance are key steps to living comfortably with this condition.